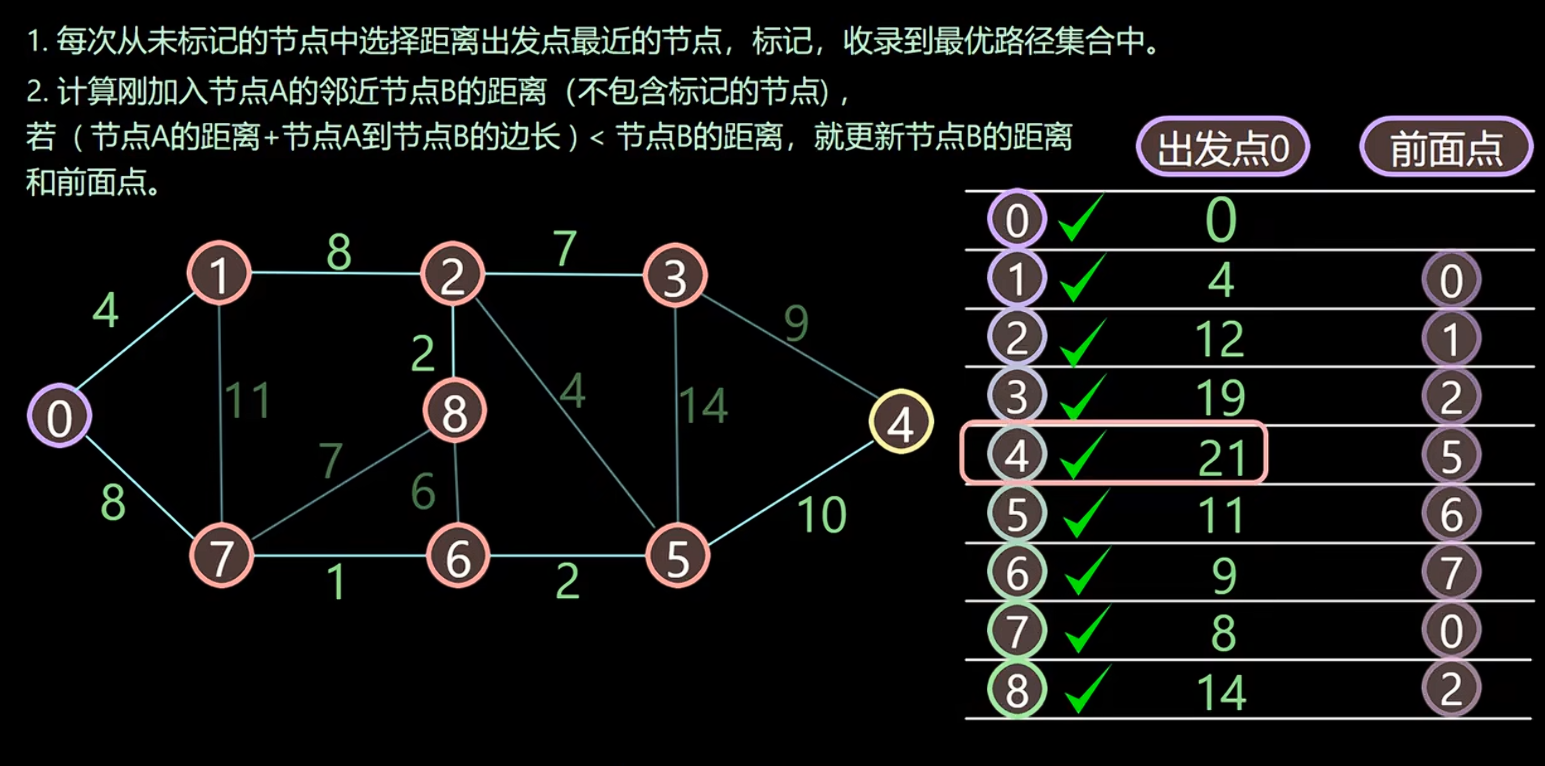
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
| import heapq
def dijkstra(graph, start):
distance = {node: float('infinity') for node in graph}
distance[start] = 0
print('distance:', distance)
priority_queue = [(0, start)]
print('priority_queue:', priority_queue)
print('graph:', graph)
while priority_queue:
current_distance, current_node = heapq.heappop(priority_queue)
print('priority_queue:', priority_queue)
if current_distance > distance[current_node]:
continue
for neighbor, weight in graph[current_node].items():
new_distance = current_distance + weight
if new_distance < distance[neighbor]:
distance[neighbor] = new_distance
heapq.heappush(priority_queue, (new_distance, neighbor))
print('priority_queue_new:', priority_queue)
return distance
graph = {
'A': {'B': 5, 'C': 3},
'B': {'A': 5, 'C': 2, 'D': 1},
'C': {'A': 3, 'B': 2, 'D': 4, 'E': 2},
'D': {'B': 1, 'C': 4, 'E': 1, 'F': 7},
'E': {'C': 2, 'D': 1, 'F': 3},
'F': {'D': 7, 'E': 3}
}
start_node = 'A'
shortest_distances = dijkstra(graph, start_node)
print("从节点 {} 出发到各节点的最短距离:".format(start_node))
for node, distance in shortest_distances.items():
print("到节点 {}: {}".format(node, distance))
|